HP Bowl type mills
key word:Heat exchange element
Category:
Product description
HP bowl mill
1. Introduction
1.1. Purpose
It is mainly used for grinding, drying and separating raw coal into qualified fineness for steam boiler combustion in thermal power plant.
1.2. Model meaning
HP ** × 3-Dyn
HP -- bowl mill
**----Nominal diameter code of grinding bowl
3 -- number of grinding rolls
Dyn --- with dynamic separator (without label with static separator)
1.3. Structural features
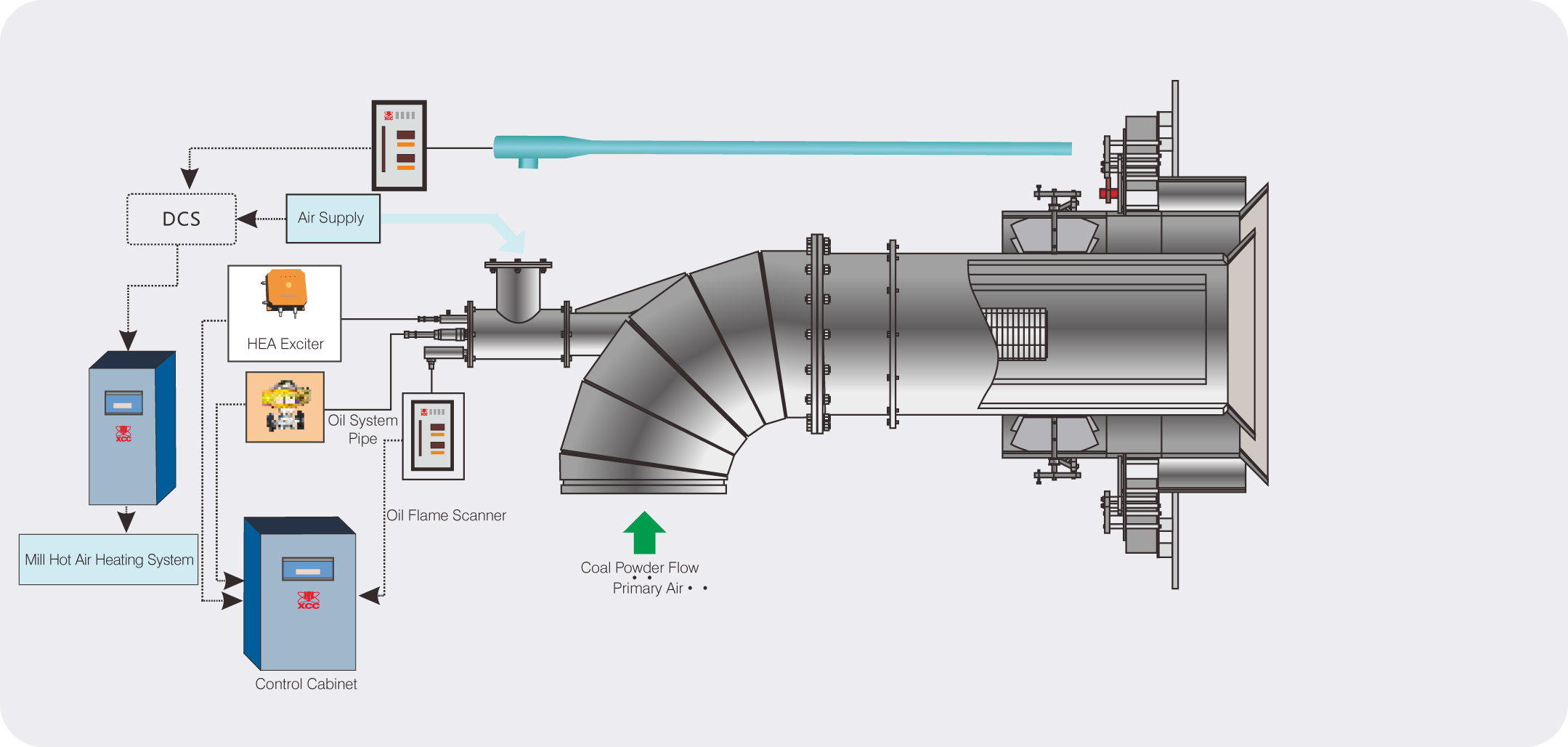
The structure of HP bowl type coal mill is bowl shaped grinding plate, three grinding rollers and spring variable loading. It is divided into HP bowl mill with static separator (see Figure 22-1) and HP bowl mill with dynamic separator (see Figure 22-2), It is mainly composed of coal falling pipe, separator top cover, inner cone, separator body (dynamic and static), impeller device, planetary gear reducer, discharge valve, folding door joint device, venturi tube, spring variable loading device, side body device, grinding bowl device, sealing air header, gravel coal outlet and other components.

The main structural features of HP bowl mill are as follows:
1.3.1. HP coal mill adopts a new type of spiral bevel gear and planetary gear two-stage reduction vertical transmission at home and abroad, and the upper part of the transmission device adopts hydraulic sliding thrust bearing to bear the grinding force of grinding rod. This form forms an independent reducer, which can be pulled out from the bottom of the mill, which is convenient for maintenance, heat insulation and sealing.
1.3.2. HP coal mill adopts mature roller surfacing technology and large diameter tapered roller. For general coal, the design life of grinding roller is more than 12000h, and it can be used repeatedly after wear, so as to reduce the cost.
1.3.3.3 HP coal mill firstly adopts impeller device rotating with the grinding bowl to change the flow direction and velocity of primary air, so as to make the air distribution more uniform through the mill, enhance the separation effect of pulverized coal, reduce the internal wear and loss of primary air resistance in the pulverizer, and improve the control ability of stone coal displacement.
1.3.4. HP coal mill adopts the patented technology of roll turning out. The roller can be turned out from its own door hole, which is very convenient for maintenance. Due to the improvement of the roller structure of HP coal mill, the roller replacement can be carried out directly on the machine, thus further reducing the downtime.
1.3.5. There is no direct metal contact between the grinding roller of HP coal mill and the lining plate of grinding bowl, so it can be started without load (or with load). Small starting torque, safe and stable operation, no coal stored in the grinding bowl during shutdown.
1.3.6. The loading mode of HP bowl mill grinding wheel adopts spring variable loading, which has the characteristics of simple structure, less maintenance, safe and reliable operation.
1.3.7. In addition to improving the fineness and uniformity of pulverized coal, the dynamic separator of HP coal mill has the characteristics of high structural reliability, simple maintenance and convenient adjustment.
1.3.8. The output of HP coal pulverizer is controlled by coal feeding rate and primary air volume. Its output regulation range is wide, and the minimum output is 25% of the maximum output, which is very suitable for peak load regulation of power plant.
1.3.9. The matching performance of HP coal mill and boiler is good. Three domestic electric group companies: Shanghai Electric, Harbin electric and Dongfang Electric's boiler plants have all introduced the boiler design technology of Alstom company of the United States, and HP coal mill is also imported from ALSTOM company of the United States, and has the characteristics of many specifications and serialization, so the matching performance of HP coal mill and boiler is good.
1.3.10. The power of motor for HP bowl mill is smaller than that of other medium speed pulverizers.
1.3.11. The ventilation resistance of HP coal mill is smaller than that of other medium speed pulverizers, and the air pressure of primary air fan is smaller, which can reduce the investment cost of fan.
1.4. Working principle
The function of HP series coal mill is to mill raw coal to achieve the fineness that can be effectively burned in the furnace. The maximum grinding output of coal mill depends on the following three factors:
A. Mill specifications.
B. The characteristics of raw coal, namely Hardgrove grindability index and water content.
C. The fineness of pulverized coal is% passing through 200 mesh sieve.
After the raw coal falls into the grinding bowl through the coal feeder, it moves outward along the radial direction under the action of centrifugal force, forming a layer of coal bed on the grinding bowl from the surface, and the coal bed passes under the grinding wheel device which can rotate around the shaft. At this time, the grinding force generated by the spring variable loading device is applied to the coal through the rotary mill, and the coal is ground into powder between the mill bowl liner and the grinding roller. The coal moving radially and circumferentially carries the broken coal powder across the edge of the grinding bowl into the conveying medium channel. The typical transport medium is hot air, which has three main functions
A. It provides necessary power for the pulverizer to separate the pulverized coal (control the fineness of pulverized coal).
B. Hot air dries coal continuously in the process of grinding, which makes coal easy to grind.
C. It is responsible for conveying pulverized coal to furnace.
In the process of coal grinding, smaller and lighter coal particles are continuously blown up from the grinding bowl by the gaseous transport medium (hot air). The conveying air can be supplied by the primary air fan at the upstream of the pulverizer or the independent powder exhauster at the downstream of the pulverizer. The primary air fan provides positive pressure and the powder exhauster provides negative pressure. Hot air enters from the side body and rises along the outer diameter of the rotating bowl. The blades (called impellers) on the grinding bowl make the air flow vertical. On the outer edge of the grinding bowl, the smaller and lighter coal particles are carried upward by the airflow, while the heavy and non grindable foreign debris pass through the air flow and fall into the side body area. Above the bowl, the lighter coal particles carried by air undergo a secondary separation process. The first stage separation occurs just above the level of the bowl. The fixed gas deflector installed on the separator body makes the heaviest coal particles change direction suddenly, lose momentum and return to the grinding bowl directly for regrinding; the lighter particles are carried by the air flow to the top cover of the separator for the second stage separation, where the curved adjustable blades make the wind powder mixture produce whirlwind motion, resulting in the heavy particles losing momentum and falling from the air flow. The heavier coal particles separated from the deflected blade and Venturi casing return to the grinding area of the bowl along the inner wall of the inner cone. The cone separates the heavy particle coal from the turbulent flow area of the coal mill, and the heavy particle coal outside the turbulent area returns to the grinding bowl under the action of gravity and is grinded again. In order to reduce the air flow velocity entering the inner cone through the inner cone mouth, an inverted cone is installed inside the inner cone, but it should be ensured that the inverted cone can not prevent the heavier coal particles from returning to the grinding bowl. When the mixture of air and powder passes through the venturi pipe, the powder in each pipe is evenly distributed, and the mixture is introduced into the furnace for combustion.
If it is a dynamic separator, after the primary separation by the deflector at the lower part of the separator body, the pulverized coal and air flow will continue to rise and enter the rotating blade rotor through the separator body. When the air flow approaches the rotor, the coal particles in the air flow will be impacted by the rotor blades, and the larger coal particles will be thrown out by the rotor, and the smaller coal particles will be allowed to pass through the rotor and enter into the rotor After entering the pulverized coal pipe, the thrown coal particles are returned to the grinding bowl to be grinded again.
Compared with the static separator, the separation efficiency of the dynamic separator has been significantly improved. As a result, the internal circulation load of the dynamic separator is smaller under the same output condition. The maximum internal circulation load of the coal mill can be achieved by increasing the load, that is to say, the maximum capacity of the coal mill is improved, or the grinding output is higher; the smaller Hardgrove grindability and the pulverized coal fineness are selected, and the grinding uniformity is improved at the same time (pulverized coal uniformity coefficient n ≥ 1.2).
The non grindable foreign debris passing through the air flow in the human side body area is scraped into the hole on the bottom plate of the grinding bowl hub skirt cover by the scraper device, and then enters the stone coal collection system. Foreign debris usually consists of rocks in coal seams and parts of mining machinery. Therefore, it is beneficial for users to minimize the amount of foreign materials entering the pulverizer.
1.5. Product series
HP type bowl pulverizer has 9 series and 30 specifications, the model is HP583-HP1303, which can be matched with 50 ~ 1000MW and above thermal power units.
2. Main technical parameters
The basic parameters of HP bowl mill with static separator and HP bowl mill with dynamic separator are shown in table 22-1 and table 22-2 respectively.
Table 22-1 basic parameters of HP bowl mill with static separator
| Model | Nominal diameter of milling bowl (mm) |
Nominal diameter of milling roll (mm) |
Feeding particle size (mm) | Basic output (t/h) |
Inlet air flow (t/h) |
Milling bowl speed (r/min) |
Motor rated power (kW) |
Weight for reference (t) |
| HP583 | 1600 | 900 | ≤38 | 15 | 22.5. | 53.4 | 160 | 60 |
| HP603 | 16 | 21.9 | 180 | |||||
| HP623 | 18.3 | 27.4 | 200 | |||||
| HP643 | 20.1 | 30.2 | 250 | |||||
| HP663 | 22.1 | 33.1 | 250 | |||||
| HP683 | 1900 | 1110 | 24.1 | 36.2 | 45.2 | 280 | 75 | |
| HP703 | 26.4 | 39.5 | 280 | |||||
| HP723 | 28.7 | 43 | 300 | |||||
| HP743 | 31.1 | 46.7 | 300 | |||||
| HP763 | 2100 | 1200 | 33.7 | 50.6 | 41.3 | 355 | 90 | |
| HP783 | 36.5 | 54.7 | 355 | |||||
| HP803 | 39.3 | 59 | 355 | |||||
| HP823 | 2200 | 1300 | 41.8 | 62.7 | 38.4 | 400 | 115 | |
| HP843 | 44.4 | 66.6 | 400 | |||||
| HP863 | 47.1 | 70.6 | 400 | |||||
| HP883 | 2400 | 1400 | 49.9 | 74.8 | 35 | 450 | 135 | |
| HP903 | 52.8 | 79.1 | 450 | |||||
| HP923 | 55.7 | 83.6 | 500 | |||||
| HP943 | 58.8 | 88.3 | 500 | |||||
| HP963 | 2600 | 1500 | 62 | 93 | 33 | 520 | 140 | |
| HP983 | 65.3 | 98 | 560 | |||||
| HP1003 | 68.7 | 103 | 560 | |||||
| HP1023 | 2800 | 1600 | 72.2 | 108 | 30 | 600 | 180 | |
| HP1043 | 75.8 | 113.6 | 650 | |||||
| HP1063 | 79.5 | 119.2 | 700 | |||||
| HP1103 | 87.2 | 130.8 | 750 | |||||
| HP1163 | 3100 | 1800 | 99.6 | 149.4 | 27.7 | 850 | 140 | |
| HP1203 | 108.4 | 162.6 | 950 | 254 | ||||
| HP1263 | 3300 | 1900 | 122.4 | 183.7 | 25.6 | 1050 | 300 | |
| HP1303 | 132.4 | 198.5 | 1150 | 305 |
Note:
1. The basic output in the table refers to the grinding capacity of coal mill under the working conditions of high volatile bituminous coal 8% and low volatile bituminous coal 12% with GHI of 55, pulverized coal fineness of 70% passing the 0.075mm sieve.
2. The maximum resistance of coal mill is 4.5kpa (plain area)
3. The service factor (S.F) of motor in the table is 1.15
Table 22-2 basic parameters of HP bowl mill with dynamic separator
| Model | Nominal diameter of milling bowl (mm) |
Nominal diameter of milling roll (mm) |
Feeding particle size (mm) | Basic output (t/h) |
Inlet air flow (t/h) |
Milling bowl speed (r/min) |
Motor rated power (kW) |
Weight for reference (t) |
| HP583/Dyn | 1600 | 900 | ≤38 | 15 | 22.5. | 53.4 | 180 | 58 |
| HP603/Dyn | 16 | 21.9 | 200 | |||||
| HP623/Dyn | 18.3 | 27.4 | 250 | |||||
| HP643/Dyn | 20.1 | 30.2 | 250 | |||||
| HP663/Dyn | 22.1 | 33.1 | 280 | |||||
| HP683/Dyn | 1900 | 1110 | 24.1 | 36.2 | 45.2 | 300 | 74 | |
| HP703/Dyn | 26.4 | 39.5 | 300 | |||||
| HP723/Dyn | 28.7 | 43 | 355 | |||||
| HP743/Dyn | 31.1 | 46.7 | 355 | |||||
| HP763/Dyn | 2100 | 1200 | 33.7 | 50.6 | 41.3 | 400 | 88 | |
| HP783/Dyn | 36.5 | 54.7 | 400 | |||||
| HP803/Dyn | 39.3 | 59 | 400 | |||||
| HP823/Dyn | 2200 | 1300 | 41.8 | 62.7 | 38.4 | 450 | 112 | |
| HP843/Dyn | 44.4 | 66.6 | 450 | |||||
| HP863/Dyn | 47.1 | 70.6 | 450 | |||||
| HP883/Dyn | 2400 | 1400 | 49.9 | 74.8 | 35 | 500 | 131 | |
| HP903/Dyn | 52.8 | 79.1 | 500 | |||||
| HP923/Dyn | 55.7 | 83.6 | 560 | |||||
| HP943/Dyn | 58.8 | 88.3 | 560 | |||||
| HP963/Dyn | 2600 | 1500 | 62 | 93 | 33 | 600 | 135 | |
| HP983/Dyn | 65.3 | 98 | 650 | |||||
| HP1003/Dyn | 68.7 | 103 | 650 | |||||
| HP1023/Dyn | 2800 | 1600 | 72.2 | 108 | 30 | 700 | 175 | |
| HP1043/Dyn | 75.8 | 113.6 | 750 | |||||
| HP1063/Dyn | 79.5 | 119.2 | 800 | |||||
| HP1103/Dyn | 87.2 | 130.8 | 850 | |||||
| HP1163/Dyn | 3100 | 1800 | 99.6 | 149.4 | 27.7 | 950 | 231 | |
| HP1203/Dyn | 108.4 | 162.6 | 1050 | 245 | ||||
| HP1263/Dyn | 3300 | 1900 | 122.4 | 183.7 | 25.6 | 1150 | 290 | |
| HP1303/Dyn | 132.4 | 198.5 | 1250 | 295 |
Note:
1. The basic output in the table refers to the grinding capacity of the coal mill under the working conditions of high volatile bituminous coal 8% and low volatile bituminous coal 12%, with the GHI of coal power of 55, coal fineness of 78.5% passing the 0.075mm sieve.
2. The maximum resistance of coal mill is 5.0kPa (plain area)
3. The service factor (S.F) of motor in the table is 1.15
3. Equipment appearance and structural dimensions
3.1. The shape and structural dimensions of HP bowl mill with static separator are shown in figure 22-3 and table 22-3

Table 22-3 structural dimensions of HP bowl mill with static separator
| Model | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L |
| HP538~HP663 | 6307 | 402 | 1047 | 1100 | 1862 | 623 | 1283 | 2019 | 2363 | 2450 | 3800 | 4035 |
| HP683~HP743 | 6387 | 913 | 925 | 1357 | 2293 | 775 | 687 | 2732 | 2819 | 2450 | 3800 | 4390 |
| HP763-HP803 | 7412 | 567 | 1077 | 1385 | 2578 | 1105 | 867 | 3214 | 2953 | 2750 | 4300 | 4685 |
| HP823-HP863 | 8075 | 1198 | 1077 | 1637 | 2635 | 1410 | 916 | 3592 | 3038 | 2472 | 3934 | 4784 |
| HP883~HP943 | 8683 | 1296 | 1226 | 1656 | 2948 | 1544 | 909 | 3910 | 3340 | 2950 | 4340 | 5045 |
| HP963~HP1003 | 8721 | 2393 | 1229 | 1686 | 2872 | 1631 | 903 | 4159 | 3400 | 2950 | 4500 | 5450 |
| HP1023~HP1103 | 9509 | 669 | 1394 | 1902 | 3396 | 1537 | 880 | 4803 | 3623 | 3200 | 5000 | 5520 |
| HP1163~HP1203 | 12062 | 778 | 1200 | 2769 | 3404 | 2360 | 1928 | 5245 | 4028 | 3400 | 5200 | 5870 |
| HP1263~HP1303 | 12953 | 700 | 1176 | 3096 | 3791 | 3420 | 1070 | 5779 | 4204 | 4000 | 6000 | 6400 |
3.2. The shape and structural dimensions of HP bowl mill with dynamic separator are shown in Figure 22-4 and table 22-4.

Table 22-4 structural dimensions of HP bowl mill with dynamic separator
| Model | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L |
| HP538~HP663 | 6204 | 402 | 1047 | 1100 | 1862 | 641 | 1162 | 2019 | 2363 | 2450 | 3800 | 4035 |
| HP683~HP743 | 6387 | 913 | 925 | 1357 | 2293 | 750 | 850 | 2540 | 2819 | 2450 | 3800 | 4390 |
| HP763-HP803 | 7412 | 567 | 1077 | 1385 | 2578 | 815 | 880 | 2792 | 2953 | 2750 | 4300 | 4685 |
| HP823-HP863 | 8075 | 1198 | 1077 | 1637 | 2635 | 870 | 1000 | 2981 | 3038 | 2472 | 3934 | 4784 |
| HP883~HP943 | 8683 | 1296 | 1226 | 1656 | 2948 | 1167 | 1193 | 3221 | 3340 | 2950 | 4340 | 5045 |
| HP963~HP1003 | 8721 | 2393 | 1229 | 1686 | 2872 | 1168 | 1147 | 3417 | 3400 | 2950 | 4500 | 5450 |
| HP1023~HP1103 | 9509 | 669 | 1394 | 1902 | 3396 | 1190 | 1192 | 3748 | 3623 | 3200 | 5000 | 5520 |
| HP1163~HP1203 | 10689 | 721 | 1200 | 2769 | 3404 | 1213 | 1703 | 4166 | 4028 | 3400 | 5200 | 5870 |
| HP1263~HP1303 | 11047 | 1000 | 1176 | 3096 | 3791 | 1448 | 750 | 4394 | 4204 | 4000 | 6000 | 6400 |
4. Selection method
The selection method of standard HP coal pulverizer can adopt computer software for accurate and detailed selection. Users only need to provide raw coal data, boiler coal consumption, pulverized coal fineness and number of coal mills to the manufacturer, and the professional technical personnel of the manufacturer will feed back the selection results to the users; Some boiler plants introduce the boiler design technology of Alstom company in the United States, and the selection software of HP coal mill is embedded in the boiler performance calculation program to select the type; in addition, users can calculate the grinding output of HP coal mill according to the following formula and chart, and preliminarily select the model of HP coal mill.
The output calculation formula of HP coal mill is
BM=BM0ƒHƒRƒM
Where BM0 ------ the basic output of the coal mill, t/h, as shown in Figure 22-5;
ƒH, ƒR, ƒM ------- the correction coefficients of Hardgrove grindability, coal fineness and raw coal moisture, as shown in Fig. 22-6.

4.1. The HP bowl mill with static separator and HP bowl mill with dynamic separator correspond to different pulverized coal fineness correction factors. Generally speaking, when the required pulverized coal fineness R90 ≤ 16%, HP coal mill with dynamic separator is recommended.
4.2. Before the moisture correction of raw coal, the coal types should be classified. Coal classification is shown in table 22-5.
Table 22-5 coal classification
| Coal type | Calorific value of water bearing mineral free basis (MJ/kg) |
Dry mineral free fixed carbon (%) |
| High calorific value coal | 32.6~37.2 | 40~86 |
| Low calorific value coal | 25.6~32.6 | 40~69 |
| Sub bituminous coal | 19.3~25.6 | 40~69 |
| lignite | 19.3 | 40~69 |
The calorific value of water bearing non mineral basis is calculated according to the following formula, i.e.

Dry mineral free fixed carbon is calculated according to the following formula, i.e.

Where Q ------------------------------Water bearing, no mineral base heat, MJ / kg;
FCdmmf --------------------Dry mineral free fixed carbon,%;
Qgr,ar -----------------------As received high calorific value, MJ / kg;
Sar,Mar, Aar, FCar ------ As received basis sulfur, moisture, ash and fixed carbon,%;
Var --------------------------As received basis volatile matter,%
4.3. If the coal belongs to high calorific value coal, when Mar ≤ 48%, the output of coal mill does not need to be corrected; otherwise, the output needs to be corrected. If the coal belongs to low calorific value coal, the output of coal mill does not need to be corrected when Mar ≤ 12%; otherwise, the output needs to be corrected.
4.4. For sub bituminous coal and lignite with total moisture greater than 20%, in addition to considering the factors such as Hardgrove grindability index and required fineness of pulverized coal, the ventilation rate and drying output of the coal mill must be checked and calculated. When grinding bituminous coal and lignite with high moisture content, two points should be paid special attention to
4.4.1. Regardless of the fineness of pulverized coal (R90 > 23%) and the Hardgrove grindability index (HGI > 55), the maximum output of the pulverizer is generally not greater than the basic output of the mill, that is, ƒH, and ƒR in the above formula are taken as 1.0
4.4.2. The final determination of the type and output of the coal mill depends on the following parameters: ① the drying dose of the pulverizer population; ② the temperature of the desiccant at the inlet of the pulverizer (generally up to 400 ℃); ③ the moisture content of the pulverized coal at the outlet of the pulverizer; ④ the outlet temperature of the pulverizer (at least 5.5 ℃ higher than the dew point temperature of the pulverized coal); ⑤ the maximum ventilation capacity of the pulverizer; and; ⑥ The maximum dry moisture of pulverized coal at the outlet of coal mill is 70% of the total moisture of raw coal
5. Scope of supply and ordering instructions
The scope of supply of standard HP bowl mill is from separator outlet flange to pebble coal hopper discharge outlet, primary air inlet flange and coal feed inlet flange. It includes coal mill body, reducer, motor, coupling, anchor bolt, mounting base plate, lubrication system, sealing fan and special tools. If the user has other requirements, they can also be negotiated in the contract.