DFBC rotary flue heat exchanger (GGH)
key word:Heat exchange element
Category:
Product description
EBC rotary flue heat exchanger (GGH)
1. Introduction
1.1 purpose
It is mainly used in power plant boiler desulfurization system.
1.2 model significance
GGH-****/####
GGH - flue heat exchanger
****---------Diameter of flue heat exchanger (mm, determined according to engineering requirements)
####------------Height of heat exchange element (mm, determined according to engineering requirements)
1.3. Working principle of flue heat exchanger
Rotary flue heat exchanger (hereinafter referred to as GGH) uses untreated flue (raw flue) and treated flue (net flue) from thermal power plant to flow through two adjacent flue ducts from bottom to top and from top to bottom respectively. When the original flue flows through the rotor, the original flue releases heat to the heat storage element, and the temperature of the original flue decreases; when the heat storage element rotates to the net flue side, the heat is released to the net flue, and the net flue temperature increases. In this way, the heat exchange between the original flue and the net flue is realized.
1.4. Structural features
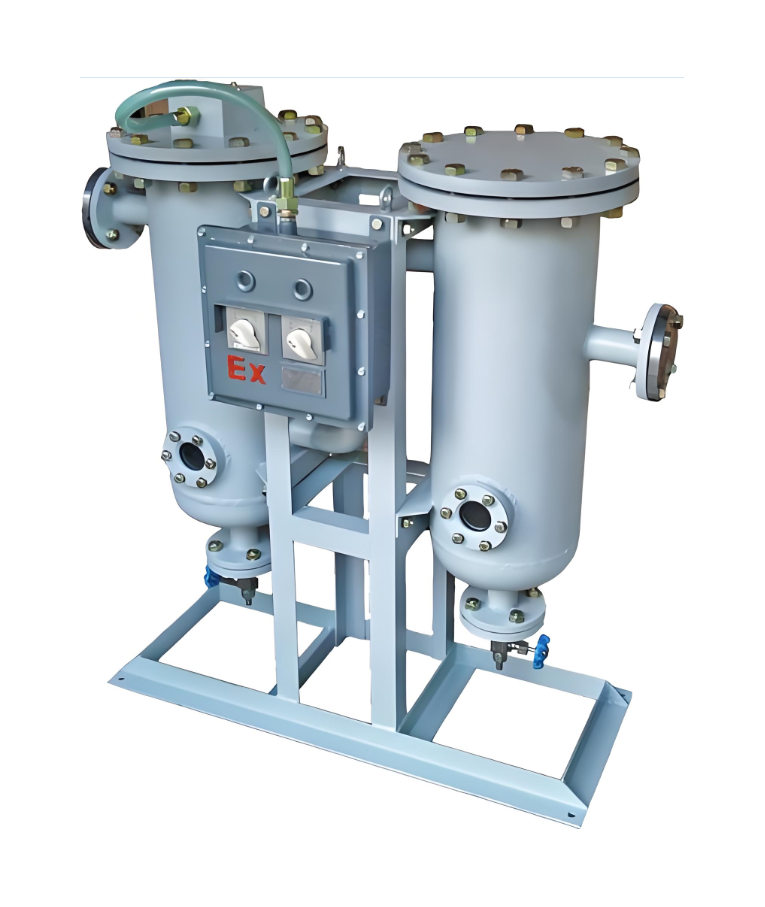
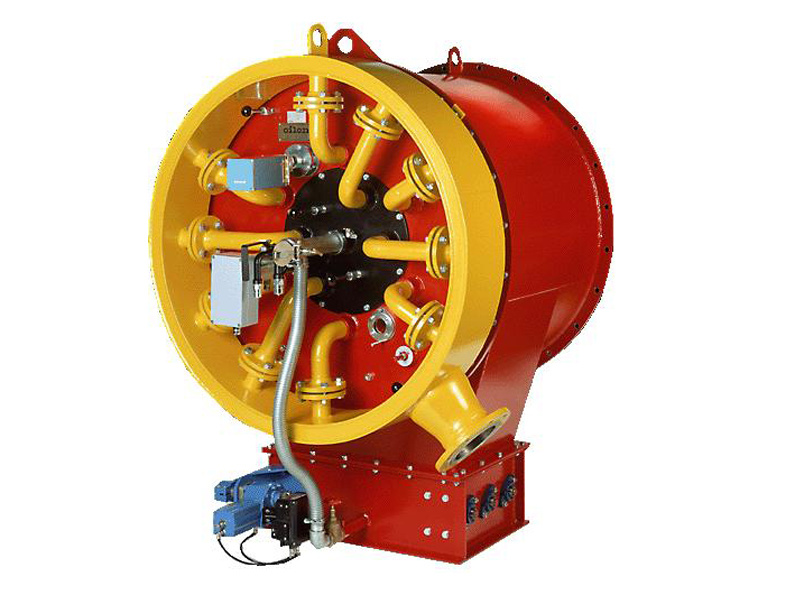
1.4.1. Structure of flue heat exchanger. GGH equipment is mainly composed of rotor, rotor seal, shell, upper beam, lower beam, heat exchange element, thrust bearing, guide bearing and rotor drive device. GGH is also equipped with soot blowers, which are installed in the upper and lower flue side of the original GGH. Compressed air and high-pressure water are used to purge the accumulated dust on the surface of heat storage elements during operation. The low pressure cleaning pipe is installed on the upper and lower flue of the original flue side of GGH to clean the heat storage elements during the shutdown of GGH. In addition, GGH is equipped with low leakage fan and sealing fan to reduce GGH flue leakage.
1.4.2. Heat exchange elements of flue heat exchanger. The self-developed DUF board type is adopted in EBC.
1.4.3. Rotor seal. The rotor seal is arranged between the original flue side and the clean flue side to reduce the flue leakage caused by the pressure difference between the original flue and the net flue. As a whole, the rotor seal is composed of radial seal, rotor central cylinder seal, bypass seal and axial seal. The cold state clearance is set in advance between the fixed sealing element and the rotor sealing plate to ensure that the thermal deformation of the rotor always keeps a minimum sealing clearance during the hot operation of GGH. By using the seal, the leakage of flue can be reduced to the minimum, and the best sealing performance can be obtained.
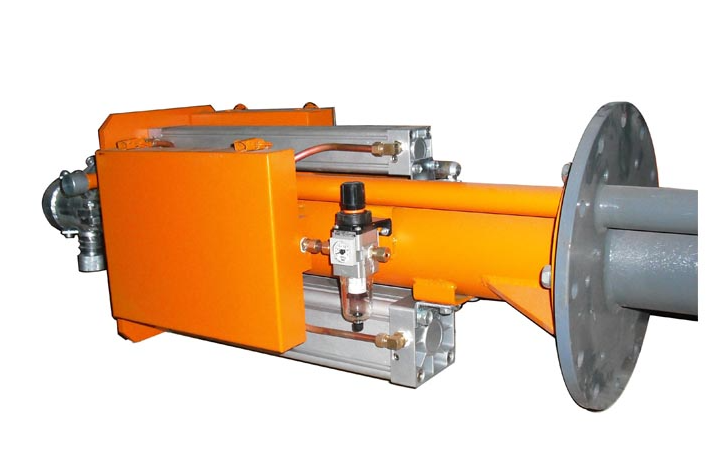
1.4.4. Driving device of flue heat exchanger. The driving motor maintains the rotation of the flue heat exchanger by meshing the big gear of the output shaft of the reducer and the shroud pin of the rotor of the flue heat exchanger. Each reducer is equipped with main motor and auxiliary motor. The main motor adopts the general power supply of the factory, and the auxiliary motor adopts the security power supply: the main and auxiliary motors are electrically interlocked, and the other one is put into operation automatically when one fails. In the process of GGH low-pressure water cleaning, the auxiliary motor is used to drive the rotor, and the speed of GGH rotor is 0.45r/min at low speed
1.4.5. Cleaning device. Two medium soot blowers are arranged at the upper and lower parts of the flue heat exchanger, that is, compressed air and high-pressure water are used as soot blowing media. The pressure of compressed air (low-pressure medium) is 0.8MPa, and the pressure of high-pressure water (high-pressure medium) is 10MPa. Fixed low-pressure cleaning water pipes are arranged at the upper and lower parts of the original flue side of the flue heat exchanger to clean the flue heat exchange gas after shutdown.
2. Equipment appearance and structural dimensions
See Fig. 5-1 for equipment outline of rotary flue heat exchanger and Table 5-1 for corresponding structural dimensions

Table 5-1 Main outline dimensions of the rotary flue heating exchanger
| Unit capacity (MW) |
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | R |
| 300 | 7035 | 12550 | 4600 | 1615 | 1885 | 1220 | 1700 | Based on the project | 2135 | 13494 |
| 600 | 9170 | 16640 | 6415 | 1905 | 2457 | 1420 | 2085 | Based on the project | 2565 | 17286 |
3. Selection method
According to the required data, site conditions, supply scope and requirements of flue heat exchanger selection.
4. Scope of supply and ordering instructions
4.1. Scope of supply (standard range, which can be deleted according to the needs of users)
The scope of supply includes product design, procurement, manufacturing, factory testing, installation and commissioning drawings, operation and maintenance manuals.
4.1.1. Devices and equipment: including rotary flue heat exchanger body, driving device and turning gear device, metal outer guard plate, soot blowing device, cleaning device, shutdown alarm device, special tools, etc.
4.1.2. Scope of supply: from the inlet flue flange of the flue heat exchanger to the flue flange at the outlet of the flue heat exchanger, including the inlet of soot blower, some cleaning pipes (including matching flange and accessories), all motor power parameters and compressed air interface.
4.2. Ordering instructions
Users need to provide the following information for reference: heat exchange elements, form and quantity of soot blowers, drive device form, bearing form, leakage value (within 1 year / after 1 year), requirements for flue heat exchanger to prevent low temperature corrosion and blockage, equipment overhaul and maintenance, form, control and instrument of thermal insulation and external guard board.